Tonsillitis and Recurrent Sore Throats

What is Tonsilitis?
Tonsillitis — inflammation of the tonsils — is a common cause of sore throats, especially in children but also in many adults. While most episodes are short-lived and resolve with rest or antibiotics, some people suffer from frequent, severe, or prolonged infections that affect their quality of life, school or work attendance, and sleep.
Mr Patel offers a balanced and evidence-based approach to the assessment and treatment of recurrent sore throats, including tonsillectomy when indicated.
What are Tonsils?
The tonsils are two small lymphoid tissues located at the back of the throat. They form part of the immune system, helping the body respond to infection — particularly in early life.
However, in some individuals, the tonsils themselves become repeatedly infected or chronically inflamed, causing more harm than benefit.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms of Tonsillitis
- Sore throat (often severe and one-sided)
- Pain when swallowing
- Fever and malaise
- Swollen, red or pus-covered tonsils
- Tender neck glands
- Halitosis (bad breath)
When Is Tonsillitis a Problem?
Tonsillitis may warrant further investigation or treatment if you or your child experience:
- Five or more infections per year
- Multiple courses of antibiotics
- Difficulty eating or drinking during episodes
- Sleep disruption due to enlarged or infected tonsils
- Time off school or work
- Quinsy (a deep abscess around the tonsil)
In some cases, the issue may be chronic tonsillitis, where the tonsils remain enlarged, inflamed or foul-smelling between episodes, or where discomfort lingers for weeks.
Treatment Options
Most cases of tonsillitis are caused by viruses and resolve with rest and hydration. However, for patients with recurrent or problematic tonsillitis, Mr Patel may recommend:
- Further investigations (e.g. blood tests)
- Referral for sleep studies if symptoms suggest obstructive sleep apnoea
- Tonsillectomy – surgical removal of the tonsils
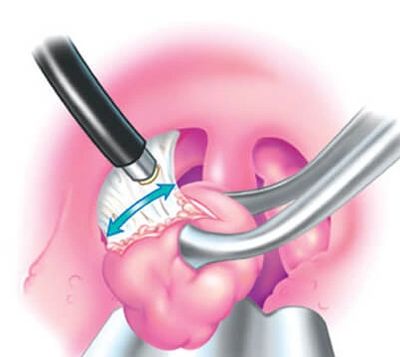
Types of Tonsillectomy
Several surgical techniques can be used to remove the tonsils. The choice depends on patient age, symptoms, and clinical findings. Mr Patel discusses the options with each patient to select the most suitable approach:
- Cold steel dissection – the tonsils are removed using surgical instruments (scalpel and scissors). This traditional method is effective but may be associated with more post-operative discomfort and bleeding in some cases.
- Bipolar diathermy – uses heat and electrical current to remove the tonsils and seal blood vessels at the same time. It reduces intraoperative bleeding but may cause more tissue damage and pain during recovery.
- Coblation tonsillectomy – uses low-temperature plasma energy to dissolve tissue precisely, with minimal heat spread. Mr Patel uses coblation for both children and adults, and tailors the approach to each patient:
- Intracapsular coblation (removing most of the tonsil while leaving the capsule intact) may offer less pain and quicker recovery
- Extracapsular coblation (complete removal of the tonsil and capsule) is preferred when tonsillitis is deeply embedded or longstanding
Coblation is the preferred technique in Mr Patel’s practice, balancing surgical precision, safety, and patient comfort.
Conservative when possible, surgical when needed
Philosophy
Mr Patel prioritises conservative management first, especially in children. But when the impact on quality of life becomes significant, he offers safe and efficient access to tonsillectomy, with recovery plans tailored to minimise pain and downtime.
What Makes us Different?
Mr Patel’s practice offers:
- A comprehensive review of each patient’s symptoms, medical history, and quality-of-life impact
- Shared decision-making, balancing the risks and benefits of surgery based on the individual’s needs
- Coblation tonsillectomy for both children and adults – a technique that uses controlled, low-temperature plasma energy to remove tonsil tissue with:
- Less thermal injury than traditional methods
- Reduced post-operative pain
- Quicker return to normal eating and activities
- Tailored surgical technique, offering either:
- Intracapsular coblation (partial removal, often preferred in young children to reduce pain and bleeding risk), or
- Extracapsular coblation (complete tonsil removal, often preferred in adults or where infection is deeply embedded)
- Day-case surgery with rapid discharge and a smooth recovery pathway
- Detailed post-operative support including pain management advice, dietary recommendations, and clear timelines for return to school or work
- Access to child-friendly settings, family-focused scheduling, and high-quality surgical facilities
Copyright © 2026 London ENT Surgery - All Rights Reserved.